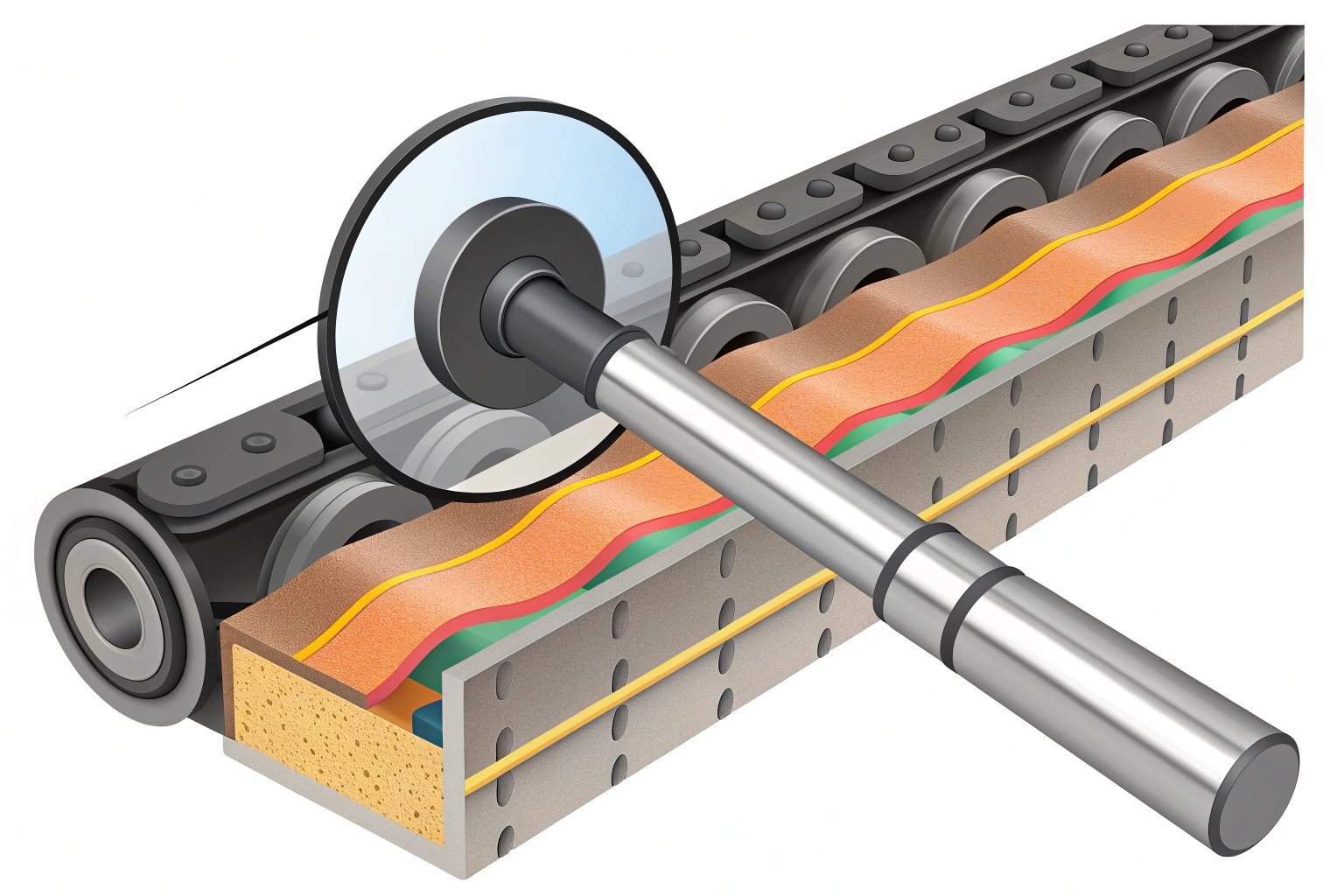
Understanding heat treatment 1 and hardness is essential for ensuring the longevity and performance of undercarriage parts 2. These specifications directly link to how well parts withstand operational demands.
To ensure parts meet required durability and performance, identify the heat treatment processes and specific hardness values (HRC) suited for undercarriage parts.
Here's how to navigate these crucial specifications.
What is the ideal surface hardness (HRC) range I should look for on a track link or roller?
The correct hardness value ensures parts resist wear without becoming brittle 3.
For track links and rollers, an ideal surface hardness on the HRC scale typically falls between 52 and 58, offering optimal wear resistance and durability.
HRC target ranges
- Track Links and Rollers: Aim for a surface hardness of HRC 53-58.
- Core Considerations: The core hardness 4 should remain lower (HRC 28–38) to retain toughness.
Key HRC values
| Component | Surface Hardness (HRC) | Core Hardness (HRC) |
|---|---|---|
| Track Link | 53-58 | 28-38 |
| Roller | 53-58 | 28-38 |
Can I ask for a copy of their heat treatment process report for my order?
Transparency in manufacturing processes indicates supplier reliability 5 and product quality assurances 6.
Yes, requesting a heat treatment process report is essential for verifying production standards and understanding how the properties align with operational needs.
Importance of process reports
- Verification: Validate that the correct procedures were implemented to achieve the desired mechanical properties 7.
- Quality Assurance: Ensures adherence to specified standards and consistency in product quality.
- Documentation: Look for details about the heat treatment applied, including temperature cycles and cooling methods.
Report inclusion
| Aspect | Purpose | Significance |
|---|---|---|
| Heat Treatment Detail | Ensures compliance | Confirms process accuracy |
| Quality Certification | Asserts standard adherence | Guarantees reliability |
| Consistency Checks | Maintains quality uniformity | Builds trust |
How do I ensure the hardness depth is sufficient for the part's durability?
The right hardness depth is crucial to maintain parts during extensive use without premature wear 8.
It's important to confirm case depth of hardness reaches an effective range, typically 4-8 mm at HRC 52+, to ensure lasting functionality in abrasive conditions.
Ensuring hardness depth
- Advocate for Testing: Request regular evaluations and case depth testing.
- Detailed Specifications: Validate depth specifications are documented and adhere to industry norms.
- Ask for Demonstrable Proof: Demand case-hardness test results reflecting adequate penetration and stability.
Hardness depth guidelines
| Depth Range | Application Suitability | Durability Impact |
|---|---|---|
| <4 mm | Light duty | Limited wear resistance |
| 4-8 mm | Standard to heavy duty | Balanced durability |
| >8 mm | Heavy impact conditions | Maximum toughness |
What are the risks if the heat treatment process is not controlled properly?
Improper process handling leads to compromised component performance 9 and rapid deterioration.
When heat treatment is not controlled, risks include inconsistent hardness, increased brittleness, and potential structural failure under stress.
Risks associated with poor control
- Variable Hardness: Leads to uneven wear or unexpected part failures.
- Structural Compromise: Incorrect procedures induce internal stresses causing cracks or fractures.
- Brittleness and Fatigue: Parts may become overly brittle or lack toughness, reducing operational lifespan.
Noted risks of improper handling
| Issue | Cause | Consequence |
|---|---|---|
| Uneven Hardening | Poor control | Part failure |
| Brittleness | Over-hardening | Increased cracking risk |
| Fatigue Weakness | Incomplete treatment | Decreased life span |
Conclusion
Grasping heat treatment and hardness nuances for undercarriage parts underpins product reliability 10 and performance in demanding conditions. Proper specifications ensure superior part utility and longevity.
Footnotes
1. Overview of metallurgical heat treatment processes for steel. ↩︎
2. Guide to identifying different excavator undercarriage components. ↩︎
3. Explains the balance between hardness (wear resistance) and toughness (brittleness). ↩︎
4. Importance of maintaining a softer, tougher core in case-hardened parts. ↩︎
5. Best practices for auditing and verifying manufacturing supplier reliability. ↩︎
6. Understanding product quality assurance systems like ISO 9001 in manufacturing. ↩︎
7. Definition of key mechanical properties in metals, including toughness and hardness. ↩︎
8. Common causes and analysis of premature wear in heavy machinery components. ↩︎
9. How material defects impact the operational life of parts. ↩︎
10. Strategies for ensuring long-term product reliability in industrial components. ↩︎